 Are you looking to migrate your VMware workloads to the cloud? Migrating virtualized workloads to the Azure VMware Solution (AVS) offers organizations a myriad of benefits, including scalability, cost efficiency, agility, disaster recovery, access to innovative technologies, and simplified management. Through the Azure cloud, organizations can modernize their IT infrastructure, drive innovation, and accelerate their digital transformation journey.
Are you looking to migrate your VMware workloads to the cloud? Migrating virtualized workloads to the Azure VMware Solution (AVS) offers organizations a myriad of benefits, including scalability, cost efficiency, agility, disaster recovery, access to innovative technologies, and simplified management. Through the Azure cloud, organizations can modernize their IT infrastructure, drive innovation, and accelerate their digital transformation journey.
For enterprises looking to migrate virtualized workloads to Microsoft Azure VMware Solution, AVS provides a fully consistent VMware platform that allows you to easily extend your on-premises VMware environment to the cloud, without the need for additional hardware or infrastructure.
In this blog, we’ll explore the architecture of VMware on Azure and how it can benefit your organization. We’ll also present why deploying external storage as a managed application on AVS can be an ideal cloud data platform for performance-sensitive workloads such as SQL or NoSQL databases.
What is Azure VMware Solution (AVS)?
AVS is a joint offering from Microsoft and VMware, combining the best of both worlds. It provides the familiarity and reliability of VMware with the scalability and flexibility of Azure. It’s a fully managed VMware environment with ongoing enhancements and upgrades. This allows you to run your existing VMware workloads in Azure without the need for any major application changes or reconfiguration.
How Does Azure VMware Solution Work?
AVS is a Hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI) service built on dedicated bare metal within Azure data centers. This infrastructure is managed and operated by Microsoft, providing you with a fully managed VMware environment.
Azure VMware Solution architecture is based on VMware Cloud Foundation. All dedicated cloud deployments will have VMware vCenter Server, vSAN (the native storage offering from VMware), vSphere, and NSX-T Data Center. This provides a consistent and familiar environment for your VMware workloads, allowing you to easily provision virtual machines (VMs) for a dedicated cloud on Azure. Each server that you deploy in AVS is running ESXi, the VMware Hypervisor, with NVMe devices.
AVS also includes Azure services such as Azure Active Directory, Azure VMware Solution Backup, and Azure Site Recovery, providing you with additional capabilities and features to enhance your deployment.
Benefits of AVS Azure VMware Solution
The Azure VMware Solution is ideal for organizations that are looking to migrate their VMware workloads to the cloud. This includes organizations that are looking for:
- Familiarity and Compatibility: AVS is built on VMware Cloud Foundation, providing a consistent and familiar environment for your VMware workloads. This allows you to easily migrate your workloads to the cloud without the need to reconfigure or change applications, or to retrain your IT staff.
- Improved Scalability and Flexibility: With AVS, you can easily scale your VMware environment in Azure to meet your changing business needs. This allows you to quickly add or remove resources as needed, without the need for additional hardware or infrastructure.
- Cost Savings: By running your VMware workloads on AVS, you can take advantage of the cost savings of the cloud. This includes pay-as-you-go pricing, eliminating the need for upfront hardware costs, reducing ongoing infrastructure costs, and easily scaling resources up or down as needed.
- Azure VMware Services: AVS integrates with various Azure services, providing you with additional capabilities and features to enhance your VMware environment. This includes Azure Active Directory for identity and access management and Azure VMware Solution Backup for data protection.
- Simplify Disaster Recovery: AVS integrates with Azure Site Recovery, providing you with a simple and cost-effective way to protect your VMware workloads in the cloud.
How to Deploy VMware on Azure
Deploying the Azure VMware Solution is a straightforward process. Here’s a high-level overview of the steps involved:
- Prepare your environment: Before deploying AVS, you’ll need to ensure that your on-premises VMware environment is compatible with AVS. This includes meeting the minimum requirements for vSphere, vSAN, and NSX-T.
- Create an AVS Private Cloud: Once your environment is prepared, you can create an AVS Private Cloud in the Azure portal. This will provision the dedicated bare-metal infrastructure for your VMware environment.
- Connect to your Private Cloud: After your Private Cloud is created, you can connect to it using a VPN or ExpressRoute connection. This will allow you to extend your on-premises network to your AVS environment.
- Deploy VMware Workloads: With your AVS environment set up and connected to your on-premises network, you can now deploy your VMware workloads to the cloud. This can be done using familiar tools such as vCenter Server or PowerCLI.
What Are the Requirements for Azure VMware Solution?
To deploy the Azure VMware Solution, you’ll need to meet the following requirements:
- On-premises VMware environment: You’ll need an existing VMware environment running vSphere, vSAN, and NSX-T. This environment must meet the minimum requirements for AVS.
- Azure Subscription: You’ll need an Azure subscription to deploy AVS. This can be a new or existing subscription.
- VPN or ExpressRoute Connection: To connect to your AVS environment, you’ll need a VPN or ExpressRoute connection between your on-premises network and Azure.
- Azure Active Directory: You’ll need an Azure Active Directory tenant to manage access to your AVS environment.
Choosing an External Storage Target for AVS
In the context of AVS, “external storage target” refers to a storage solution outside of the AVS environment that is used to store virtual machine (VM) data. When deploying VMware VMs in Azure using AVS, organizations have the option to use either Azure Disk Storage, Azure NetApp Files (ANF), Pure Storage, or Lightbits as the storage solution for their VMs. These storage solutions are considered “external” to the AVS environment because they are separate from the VMware native storage vSAN that AVS provides. Many organizations choose an external storage target because while vSAN is sufficient storage for workloads that do not require high performance or consistently low latency, it’s not ideal for performance-sensitive workloads like database and analytics.
Using external storage targets in AVS allows organizations to take advantage of the scalability, performance, and features offered by Azure storage services while running their VMware workloads in the cloud. This approach enables seamless integration between VMware environments and Azure services, providing flexibility and efficiency for managing VM data.
Enhancing AVS with Cost-Efficient, High-Performance, and Resilient External Block Storage
AVS clusters are based on hyper-converged infrastructure built on top of a set of host types with specific amounts of CPU, memory, disk, and network. While these nodes are generally effective for hosting many workloads, they are not ideal for storage-intensive workloads, such as SQL or NoSQL databases. These workloads demand high throughput, low latency, and various storage-to-compute ratios. To meet the performance and capacity demands of these workloads using vSAN would require adding nodes that you don’t require, but this subsequently increases the cost of your cloud storage and can strain your IT budget.
Lightbits cloud storage for Azure VMware Solution enhances the current storage offerings within AVS, providing the most cost-efficient external storage solution for workloads that demand high performance, consistently low latency, and scalability. Lightbits is the first NVMe® storage with VMware certification for Azure Cloud. Using Lightbits, you can create VMFS datastores backed by NVMe/TCP volumes. This combination gives you the high performance and low latency of NVMe-oF external storage with enterprise data services and all of the flexibility and scalability of VMFS. VMFS has been a popular choice because it’s specifically designed to handle the requirements of virtualization and is optimized for VM disk operations. It provides features such as file locking, thin provisioning, snapshots, and more – all of which are essential for efficiently managing VMs in VMware environments.
How to Deploy Lightbits as a Managed Application on AVS
Lightbits for Azure VMware Solution is available through the Azure Marketplace as a fully managed service. All of the data resides in your subscription, while Lightbits has access to maintain, operate, and monitor the storage for you.
As shown in the figure below, when you deploy the Lightbits Managed Application, all of the required resources are created within a managed resource group. These resources include a set of Lv3 series storage-optimized virtual machines, equipped with local NVMe devices connected to AVS using Express Route Ultra Gateway with Fast Path enabled.
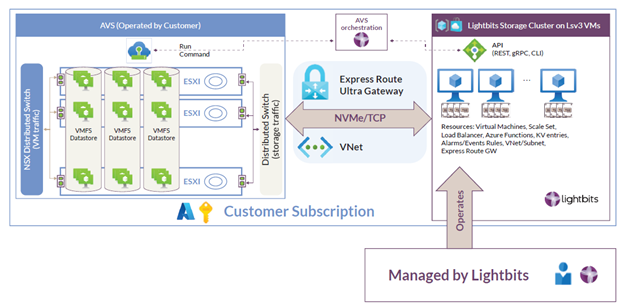
Why Lightbits for Azure VMware Solution?
Lightbits for AVS offers many advantages and benefits, including:
- The ability to efficiently run performance-sensitive virtualized applications on AVS
- Ideal for large-scale deployments of virtualized databases: SQL Server, Oracle, MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, and more.
- Scaling storage independently from compute resources
- Controlling storage costs with simple, predictable pricing
- Improving availability and enabling multi-tenancy
- Certified by VMware and fully integrated with AVS
Use Cases for AVS
Azure VMware Solution (AVS) offers several compelling use cases for organizations looking to leverage VMware-based workloads within the Azure cloud environment. Some common use cases include:
- Data Center Extension: Companies that have invested in VMware technologies on-premises can seamlessly extend their existing VMware-based infrastructure to Azure without the need for significant rearchitecting or retooling. This enables organizations to benefit from Azure’s scalability, global reach, and advanced services while maintaining compatibility with their existing VMware environments.
- Disaster Recovery: AVS provides an ideal platform for implementing disaster recovery solutions. By replicating VMware workloads to Azure, organizations can ensure business continuity and minimize downtime in the event of a disaster or service disruption. Azure’s geographically dispersed data centers and robust disaster recovery services, such as Azure Site Recovery, enhance resilience and recovery capabilities.
- Application Modernization: Organizations seeking to modernize their applications can leverage AVS as a stepping stone to cloud-native architectures. By migrating VMware workloads to Azure, companies can gradually refactor or replatform applications to take advantage of Azure’s platform-as-a-service (PaaS) offerings, containers, and serverless computing while maintaining compatibility and interoperability with existing VMware investments.
- Dev/Test Environments: AVS provides an agile and cost-effective platform for creating development and testing environments. Developers can quickly provision VMware-based VMs in Azure, enabling rapid application development, testing, and validation. Azure’s pay-as-you-go pricing model allows organizations to optimize costs by scaling resources up or down based on demand.
- Hybrid Cloud Deployments: AVS enables seamless hybrid cloud deployments by providing consistent VMware environments across on-premises data centers and the Azure cloud. This allows organizations to distribute workloads across hybrid environments based on performance, compliance, or cost considerations while maintaining centralized management and control through familiar VMware tools.
- Compliance and Security: Azure’s comprehensive set of compliance certifications and security features, such as encryption, threat detection, and identity management, enhance the security and compliance posture of VMware workloads running in AVS. Organizations can leverage Azure’s built-in security controls and compliance capabilities to protect sensitive data and meet regulatory requirements.
Overall, AVS offers organizations the flexibility, scalability, and innovation of Azure cloud services while preserving investments in VMware technologies and expertise. By addressing a variety of use cases, AVS empowers organizations to accelerate digital transformation initiatives, improve operational efficiency, and drive business outcomes in the cloud.
Conclusion
The Azure VMware Solution is a powerful offering that allows you to seamlessly deploy and run your VMware workloads on dedicated cloud infrastructure within the Microsoft Azure environment. By taking advantage of the scalability and flexibility of the cloud, while still maintaining the familiarity and compatibility of VMware, you can easily extend your on-premises environment to the cloud and achieve your business goals.
With scalable high performance, consistent low latency, and predictable low costs, the Lightbits cloud data platform enables you to migrate storage-intensive applications to AVS with success. Built with large-scale deployments of mission-critical applications in mind, Lightbits unifies resources like a SAN so you can provision and manage storage efficiently, instead of selecting from a limited set of options with fixed compute-to-storage ratios.

