This educational blog presents a high-level overview of Azure storage options for high-performance workloads. For a more technical overview start with our solutions page: Lightbits storage in Azure Cloud.
Data is the new currency and the lifeblood of organizations worldwide. From customer information to operational data, companies rely on vast amounts of information to drive decision-making and innovation. However, it’s growing at such a rate that traditional storage solutions can fall short in many aspects including dynamic scalability in response to business demand, the performance to meet the applications’ requirements, and the efficiency and flexibility to meet data center dynamics and modernization needs. Mission-critical workloads and cloud-native applications are increasingly requiring more performance, scalability, and reliability to enable organizations to extract value from their data. For these reasons, data center modernization strategies and public cloud options, like Microsoft Azure cloud storage, have come into play to support these workloads. Azure cloud storage services offer a robust platform for organizations needing to store, manage, and access their mission-critical data from anywhere in the world.
Overview of Cloud Storage Options on Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure is a comprehensive cloud computing platform that offers a wide range of services, including Azure Cloud Storage. For this blog, we’ll focus only on the high-performance cloud storage offerings on Microsoft Azure that empower organizations to harness the power of Azure to deliver exceptional performance, reliability, and scalability for their most demanding workloads. Whether it’s powering database applications, virtual machines, or containerized environments, high-performance storage solutions on Azure provide the speed and efficiency you need to succeed in today’s fast-paced digital landscape.
Azure high-performance storage consists of several services, each designed to address specific workload requirements:
- Local NVMe® devices: Azure cloud storage services offer Virtual Machines (VMs) that can be configured with local NVMe storage disks for high-performance workloads. Examples of VMs that offer local NVMe storage include Azure HBv3 Series, Azure Lsv2 Series, Azure Mv2 Series, Azure Nv4 Series, and Azure N-series.
- Azure Managed Disks: Managed Disks are an option for high-performance cloud storage in Azure. These block storage options are designed for I/O-intensive, latency-sensitive workloads. Examples include Azure Ultra Disk or Premium SSD v2.
- Elastic SAN: Organizations can leverage Azure cloud storage services to build elastic and scalable SAN architectures tailored to their specific requirements and workloads. By configuring VMs with multiple attached Azure disk storage, organizations can create storage pools and provision software-defined storage solutions to build highly available and scalable SAN architectures in the cloud.
The Advantages of Azure Cloud Storage
Organizations migrate mission-critical workloads from on-premises environments to the Azure Cloud for many reasons, including scaling services in response to unpredictable demand, the ability to quickly provision resources, and leveraging economies of scale. It also provides disaster recovery (DR) strategies that ensure high availability and data resilience.
Moreover, the pay-as-you-go pricing model for Azure cloud storage eliminates upfront infrastructure costs and allows you to optimize spending while attractively shifting CapEx costs to the OpEx budget. By migrating workloads to Azure, you can focus on core business objectives while reducing your operational overhead.
Azure Cloud Storage offers numerous benefits over legacy storage systems in on-premises data centers:
- Scalability: Storage in Azure Cloud can scale seamlessly to accommodate growing data volumes and AI-powered services. Monitoring capabilities optimize Azure cloud storage configurations to ensure you can keep pace with your expanding storage needs without worrying about capacity constraints.
- High Availability: With built-in redundancy and replication options, Azure Cloud Storage ensures your data remains accessible even in the event of hardware failures or disasters.
- Security: Azure cloud storage services provide robust security features, including encryption at rest and in transit, role-based access control, and advanced threat detection, to protect your sensitive data from unauthorized access.
- Cost-Effectiveness: flexible pricing options, allow you to pay only for the Azure cloud storage you use and to adjust capacity as needed to optimize costs.
- Global Reach: The extensive network of Azure cloud storage services enables you to store data close to your users, reducing latency and improving performance for distributed applications.
Strengths and Shortcomings for Native Storage Options on Azure
Azure offers a variety of high-performance storage options, each with its strengths and weaknesses:
- Local NVMe devices
- Strengths:
- High Performance: Local NVMe storage provides extremely fast storage performance with low latency and high throughput. This makes it ideal for workloads that require rapid access to data, such as high performance databases in the cloud, analytics, and high-performance computing (HPC) applications. With NVMe SSDs directly attached to the physical host hardware, Azure VMs with local NVMe storage can achieve exceptional I/O performance, enabling you to run demanding workloads with ease.
- Low Latency: Significantly lower latency compared to traditional storage technologies like SATA and SAS SSDs. This low latency ensures that data access operations are executed quickly, reducing application response times and improving overall system performance. By leveraging local NVMe storage on Azure VMs, you can achieve faster data processing, improved application responsiveness, and enhanced user experience for critical workloads.
- Strengths:
- Shortcomings:
- Lacks data protection: Local NVMe storage on Azure VMs is ephemeral and not persistent. This means that data stored on local NVMe disks is not replicated or backed up by Azure and may be lost if the VM is deallocated or moved to a different host.
- Scaling limitations: Local NVMe storage capacity scales with the size and configuration of the Azure VM series. While some VM series may offer larger local NVMe storage options than others, the scalability of local NVMe storage is constrained by the maximum capacity supported by the VM instance type− the capacity of local NVMe storage cannot be dynamically scaled up or down independent of the VM instance. You may encounter limitations in terms of storage capacity when deploying workloads that require extensive storage resources or data retention.
- No data services: Local NVMe storage on Azure VMs does not natively support data services like snapshots. You can implement comprehensive data management and protection strategies using a combination of Azure services, third-party tools, and application-level features to meet their specific requirements for data protection, backup, and recovery but this adds complexity and costs to manage the system.
- Shortcomings:
- Azure Managed Disks:
- Strengths:
- Simplified management: Azure Managed Disks simplify the management of storage for VMs by abstracting away the complexities of storage management, allowing your users to focus on deploying and managing VMs without worrying about underlying storage infrastructure.
- Improved reliability: Managed Disks offer built-in redundancy and fault tolerance to ensure high availability and data durability. Managed Disks are replicated within the Azure platform, providing redundancy at the disk level to protect against hardware failures and data loss. By using Managed Disks, you can ensure that your VMs have reliable and resilient storage with minimal effort and complexity.
- Shortcomings:
- Performance limitations: Azure Managed Disks have predefined throughput and IOPS limits. Your users may need to choose larger disk sizes or higher performance tiers to meet their performance requirements which increases Azure cloud storage costs. Managed Disks are hosted on shared infrastructure within the Azure platform, so your users should be aware of the potential for variability in disk performance in multi-tenant environments.
- Pay for provisioned IOPS and throughput: Ultra Disk is billed based on the provisioned size, provisioned IOPS, and provisioned throughput. You can choose the configuration that best meets your workload requirements in terms of storage capacity, IOPS, and throughput. For Premium SSD v2, disk storage capacity, IOPS, and throughput are charged separately.
- Data services: You can store incremental snapshots for Premium SSD v2 and Ultra Disk only on standard storage.
- Strengths:
- Azure Elastic SAN
- Strengths:
- Scalability: Azure Elastic SAN can scale to petabytes of data without the need for upfront investment in hardware or infrastructure. This scalability enables you to accommodate growing storage requirements and handle fluctuating workloads with ease.
- Resilience and Availability: Azure replicates data across multiple storage nodes and data centers within a region, offering features like geo-redundant storage (GRS) and zone-redundant storage (ZRS) to replicate data across multiple regions or availability zones providing resilience against hardware failures, data corruption, and other disruptions. By leveraging Azure Elastic SAN, you can achieve high levels of data availability, resilience, and durability for SAN-like deployments, minimizing the risk of data loss or downtime.
- Shortcomings:
- Performance limitations (IOPS and latency): Based on legacy, slow iSCSI storage protocol with single-digit millisecond latency, performance is limited to up to 64K IOPS and 1GB/s per volume (depending on volume capacity), and 5K IOPS per TB in the SAN (e.g 20TB SAN gives up to 100K IOPS)
- Lack of data services: Essential data services such as snapshots, clones, data reduction, and thin provisioning can be provisioned from third-party tools, but this adds complexity and costs to manage the system.
- Strengths:
Azure Managed Application for Turnkey Operations
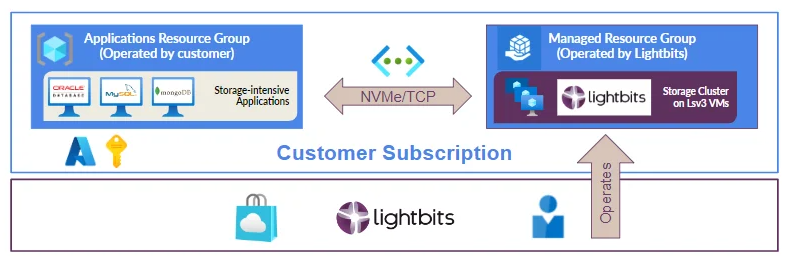
In addition to its core Azure Cloud Storage Services, Azure also offers managed applications that simplify the deployment, management, and monitoring of Azure Cloud Storage resources. Managed applications are designed to simplify the deployment and management of complex, multi-tiered applications by encapsulating all the necessary resources, configurations, and dependencies into a single package.
Lightbits block storage on Azure is available through the Marketplace as a Managed Application, making it as easy to provision and manage as Azure’s native cloud storage offerings. You choose the size of the virtual machines and the number of nodes in your cluster and you’re ready to go. As a fully managed service, Lightbits controls operations within your Azure subscription and manages the storage with self-healing, auto-scaling, replication, rolling upgrades, and other critical functions performed behind the scenes to ensure availability, performance, and data protection. By leveraging this managed block storage in the cloud solution, you can reduce operational overhead, improve resource utilization, and accelerate time-to-value.
Pricing Models for Azure Cloud Storage
Azure Cloud Storage Services are offered with flexible pricing options to suit different budget and usage requirements:
- Pay-As-You-Go: With pay-as-you-go pricing, you pay only for the storage and data transfer you use, with no upfront costs or long-term commitments.
- Reserved Capacity: Reserved capacity pricing allows you to pre-purchase Azure Cloud Storage capacity at discounted rates, providing cost savings for predictable workloads with consistent storage needs.
- Volume Discounts: Azure offers volume discounts for customers with large-scale storage requirements, providing additional cost savings based on usage volume.
- Enterprise Agreements: Enterprise agreements enable you to negotiate custom pricing and terms based on your specific storage needs and usage patterns.
By choosing the right pricing model for their storage requirements, you can optimize costs and maximize the value of their Azure Storage investment.
Note that if you use Premium Azure Cloud Storage for high performance, then you will pay for provisioned IOPS. You can provision as many Managed Disk configurations as you need to achieve the performance your applications require, but each volume will have the IOPS and throughput limitations mentioned above. This means that you are provisioning resources with performance and capacity coupled together—which can result in overspending on resources (compute or storage) that are not necessarily needed. Reference the screenshots from the Microsoft website below (source: Microsoft Managed Disks Pricing website)
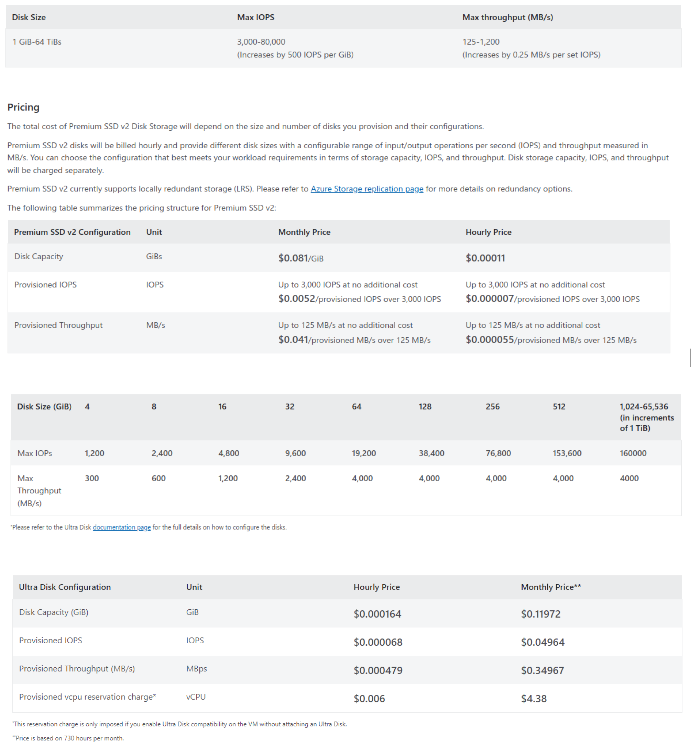
Source: Microsoft Azure Managed Disks pricing website (https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/pricing/details/managed-disks/)
Use Cases for High-Performance Azure Cloud Storage
Azure Cloud Storage is well-suited for a wide range of use cases across industries, including:
- E-commerce: Azure can be leveraged for e-commerce storage to store product images, catalogs, and user-generated content for online retail, with built-in CDN integration for fast, scalable delivery to global audiences.
- Media and Entertainment: Azure Cloud Storage is ideal for storing and serving media files, such as videos, music, and images, with low latency and high throughput for streaming and Content Delivery Networks (CDN).
- IoT and Telemetry: Azure Cloud Storage is well-suited for storing telemetry data from IoT devices, such as sensor readings, device logs, and event streams, with fast ingest and query capabilities for real-time analytics and monitoring.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery: Azure provides a reliable, cost-effective solution for backing up on-premises and cloud-based workloads, with automated backup policies, incremental backups, and offsite replication for data protection and recovery.
- Big Data Analytics: Azure is designed for storing and analyzing large volumes of structured and unstructured data, making it ideal for big data analytics, machine learning, and data warehousing workloads.
- Azure VMware Solution: For organizations looking to migrate virtualized workloads to the cloud, Azure VMware Solution (AVS) provides a fully consistent VMware platform that allows them to ‘lift and shift’ to Azure without time-consuming, expensive application refactoring.
In conclusion, Microsoft Azure offers a full range of native cloud storage solutions for a powerful and flexible platform for storing, managing, and analyzing data in the cloud. With its scalability, reliability, security, and cost-effectiveness, Azure Cloud Storage enables organizations to unlock the full potential of their data and drive innovation across their business operations. Whether serving media files to global audiences, analyzing telemetry data from IoT devices, or protecting critical workloads with automated backups, Azure Cloud Storage has a solution to meet every storage need.
But if you are cost-sensitive and need high-performance cloud storage for your applications investigate third-party solutions in the Marketplace, such as the Lightbits cloud data platform. With Lightbits, you migrate and run your most demanding performance-sensitive workloads on Azure with predictable and low costs. We are so confident that we can lower costs for premium cloud storage on Azure that we guarantee it. Let us demonstrate the unique value and lower TCO advantages of Lightbits on Microsoft Azure–find out more about our Cloud Quickstart Kit today.
Additional learning materials:

